The content of the article:
- Views
- Device
- Principle of operation
- Major breakdowns
- Pros and cons
- Parts price
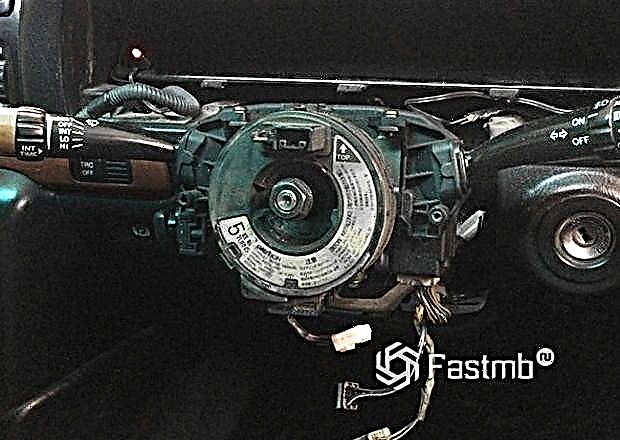
The steering wheel angle sensor is designed to determine the position of the steering wheel in the range of 720 degrees to each side (left or right). Most often, the manufacturer places such a sensor on the steering column, under the steering wheel itself. Much less often, such a mechanism is installed on the distributor shaft or above the column shaft itself. Let's consider what the mechanism is intended for, its structure and principle of operation.
A variety of steering wheel sensors

Today, few motorists can be surprised by the presence of a steering wheel angle sensor, but few can understand the importance of the mechanism and its varieties. It is on this sensor that the control of the steering mechanism, as well as auxiliary safety and comfort systems, depends. The main task of such a mechanism is to read the steering angle. Also, the calculation of the direction of the steering wheel, and at what speed the steering wheel of the car turns.
In turn, the sensor is connected to the electric power steering control unit. The latter, depending on the received data of the element, corrects the operation of the amplifier electric motor. It is such a serviceable element that guarantees the operation and accuracy of the entire electric power steering. As a rule, the following safety systems are associated with the steering wheel angle mechanism:
- adaptive cruise control;
- exchange rate stability system;
- adaptive lighting (high beam switching and oncoming traffic control);
- lane departure assistant;
- active (adaptive) car steering;
- active suspension (steering mechanism).

As for the variety of steering wheel angle sensors, experts distinguish three main types that can be found today. The principle of operation and design of such elements is significantly different:
- optic;
- potentiometric;
- magnetoresistive.
Let's consider each of the types in order to understand what is the main difference and how the principle of operation differs.
How does the steering wheel turn sensor work?

The simplest among the three listed options is considered a potentiometric sensor, it belongs to the category of contact mechanisms. The basis for this type of element is two potentiometers, which are most often installed on the steering column of a car. For the correct operation of this type of mechanism, one of the installed potentiometers is shifted 90 degrees relative to the other.

The last, third type of the steering wheel angle sensor is magnetoresistive. It is this type of elements that are most often found in modern cars and have a minimal percentage of breakdowns and shortcomings. Like the previous two types of elements, it also measures the direction, frequency and angle of the steering wheel of a car. Thanks to the device, the electronic control unit more accurately determines the data and sets the speed of the electric power steering.
The list of magnetoresistive elements includes housing, magnetoresistors, as well as moving magnets. The central part of the element is occupied by large magnetoresistors, also known as GMR elements or their analogs anisotropic magnetoresistors, marked as AMR. Due to the presence of a gear train in the mechanism, the moving magnets can rotate. An interesting fact is that each subsequent gear wheel in the sensor mechanism has one tooth more than the previous one, so it is worthwhile to clearly maintain the alignment of the installation during repairs.
How does the steering wheel turn sensor work?
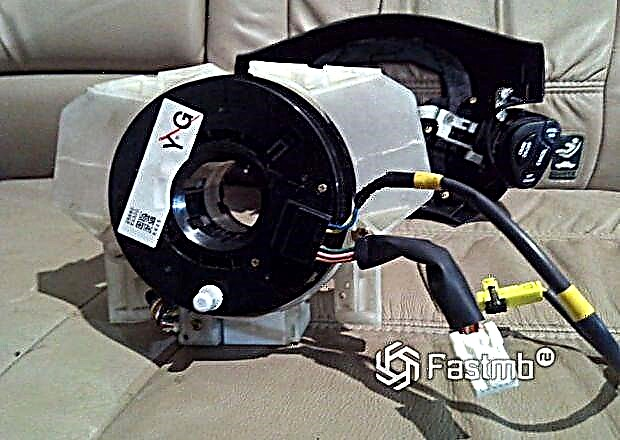

First on the list is a potentiometer-based steering wheel angle sensor. Above, the device of such a mechanism has already been considered, as for the principle of operation, it is simple, with an increase in the angle of rotation of the steering wheel, the resistance on the potentiometer increases. The resistance of the element is proportional to the steering angle.
The advantage of this type is the simplicity of the design, but with the minuses it is an unreliable design. Most often, a potentiometric sensor is installed on budget models or even trying to eradicate it from the steering mechanism. Accordingly, it is very rare on modern cars.
Second sensor - optical, its principle of operation is much more complicated than the first, but, accordingly, the quality of work is much better. The main function of the work is performed by the coding disc, which is attached to the steering column shaft of the car. The disc includes outer and inner rings. Typically, there are several uniform holes on the inner ring, and uneven holes on the outer ring.
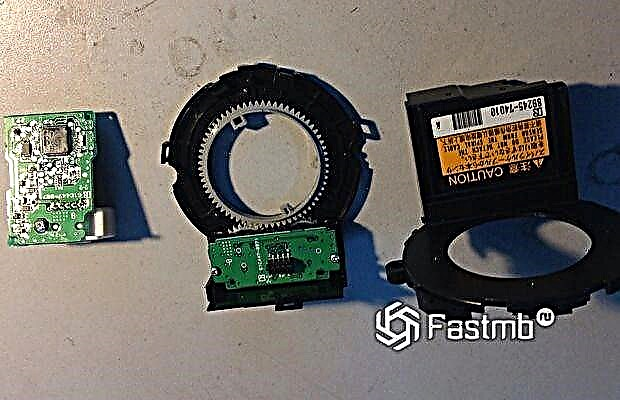

It is due to this arrangement of the holes that the arrangement of the inner ring makes it possible to determine at what angle the steering wheel is turned. The outer ring allows the element to determine which direction the rudder is turning. To remove information, engineers installed LEDs between the rings, and photoresistors (in other words, a transmitter and a receiver) are installed on the outside of the rings. How many LEDs and photoresistors are installed on the sensor depends on the manufacturer and model. The principle of operation of such a sensor is not complicated, when the driver turns the steering wheel, the light from the LEDs hits the photoresistors. At this moment, the electrical circuit generates voltage, the holes in the rings interrupt the light beam, and the voltage changes accordingly. The electronic control unit reads data on the appearance of voltage pulses, their frequency and code (because of this, the parts are called the code disk). In accordance with the received data, the steering direction and the steering wheel angle of the vehicle are calculated. It is due to such a device that optical sensors are found more often in modern cars.
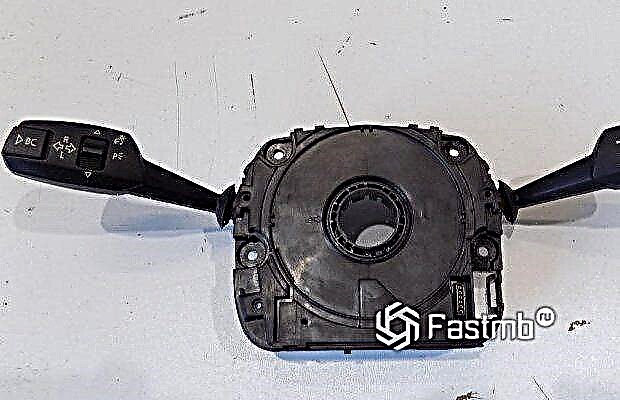

The last type of sensors, the principle of operation of which is worth considering, is magnetoresistive. Unlike the previous two elements, this type of work is more difficult. Each turn of the steering wheel receives its own specific position of the moving magnets of the element. In turn, the magnetoresistors determine the position of the moving magnets and transmit information to the electronic control unit. Based on the data received, the ECU calculates the steering angle, speed, and direction. Due to this arrangement and precision of work, magnetoresistive elements are considered the most reliable and widespread in modern cars.
What are the breakdowns of steering sensors

As they say, there is nothing perfect, respectively, and the steering wheel angle sensors also fail. Since this is an electromechanical unit of a car, it is much more difficult to determine a breakdown and a driver without experience will simply not be able to understand whether a working element is or not. The weakest points of such elements are wiring and metal elements, since they are constantly mobile.
A common problem can be the boot on the camshaft. In the event of a breakdown, the shaft begins to rust, untimely elimination of the problem can bring rust to the sensor, which means that it will quickly fail. Dust and moisture are equally detrimental to the steering angle mechanism. This is especially true when the mechanism is located on the steering rack. As practice shows, in most cases, the first to fail is the electrical circuit or the electronics itself.This situation is much worse than all the others, at best the sensor will completely fail, at worst it will transmit false data and incorrectly determine the rudder angle, direction and speed.

Whatever the type of steering angle element is, it is a precise and fragile mechanism. Experts say: if the physical zero shifts, the geometry is broken or the battery is disconnected, then the readings of the angle element may not be accurate. There are several ways to determine a breakdown or malfunction of the steering angle sensor. The first is an indicator on the instrument panel, yellow is a sign of an operating error, red is a complete shutdown of the mechanism. The indicator itself looks like a steering wheel, it can blink or be constantly on.
A few more signs of a malfunction of the steering wheel angle mechanism - tight rotation of the steering wheel, it can rotate in jerks, dips appear, or it jerks from side to side. The most common sign of sensor breakage is a delayed wheel turn response to a steering wheel turn, resulting in the car driving from side to side.
Pros and cons of having an angle sensor

The presence of a steering angle sensor in a car is always a plus. Firstly, an electric power steering will be installed in parallel, and secondly, many active safety systems can be installed on board the car. For example, a lane monitoring system, adaptive cruise control and others. The system fulfills the assigned tasks, accurately follows the instructions of the driver and improves the safety of the vehicle.
Among the disadvantages of the steering wheel angle sensor is the possibility of quick failure at the most inopportune moment. In the event of a breakdown, many talk about expensive maintenance, and in most cases it will be necessary to go to a special service center. In other words, if the steering angle element fails, then it is almost impossible to repair it on your own, or you need to look for a donor. Also, the minus is that, like any electronics, over time, the mechanism may begin to malfunction, which means that other active security systems will work poorly.
Car steering angle sensor price

The cost of a car steering wheel angle sensor largely depends on the brand, model, as well as on the type of element itself. The same mechanism will not appear to fit different cars. Car manufacturers make various fasteners, contact strips and other tricks to minimize the possibility of self-repair or replacement.
| The approximate price of the steering angle sensor | |
| Car make and model | Price from, $ USD |
| Opel Vivaro | 30 |
| Mercedes-Benz ML | 100 |
| Lexus RX300 / 330/350/400 | 80 |
| Subaru Forester S12 2007 | 110 |
| Mercedes-Benz Vito W639 | 16 |
| Nissan leaf | 81 |
Prices are for magnetoresistive sensors. Despite the fact that the structure of the structure and the principle of operation are the same, in appearance they differ significantly, and in the same way they differ in fasteners. Whether the presence of such a sensor in a car is positive or negative is the opinion of everyone. As statistics and practice show, most car manufacturers introduce such a mechanism, since active safety systems are built on its basis. Accordingly, it is easier for the driver to drive and safety is improved.